| CD44 |
|---|
 |
| Structure de la protéine CD44. Basé sur l'identifiant PDB 1poz. |
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
1POZ, 1UUH, 2I83, 4PZ3, 4PZ4 |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | CD44 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 107269 MGI: 88338 HomoloGene: 508 GeneCards: CD44 |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 11p13 | Début | 35,138,882 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 35,232,402 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 2 E2|2 54.13 cM | Début | 102,641,486 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 102,732,010 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
| Fortement exprimé dans | - parotide
- stromal cell of endometrium
- vulve
- pénis humain
- skin of abdomen
- tendon calcanéen
- îlot de Langerhans
- artère temporale superficielle
- jointure synoviale
- thymus
|
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - molaire
- calvaria
- derme
- glande submandibulaire
- parotide
- corps du fémur
- lobe pulmonaire droit
- follicule pileux
- skin of abdomen
- cornée
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
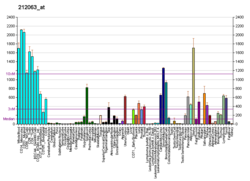
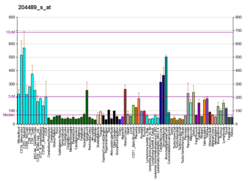 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - collagen binding
- liaison protéique
- hyaluronic acid binding
- cytokine receptor activity
- transmembrane signaling receptor activity
| | Composant cellulaire | - integral component of membrane
- appareil de Golgi
- macrophage migration inhibitory factor receptor complex
- membrane
- focal adhesion
- membrane plasmique
- integral component of plasma membrane
- surface cellulaire
- exosome
- cytosol
- secretory granule membrane
- apical plasma membrane
- lamellipodium membrane
- prolongement cellulaire
- microvillosité
- basolateral plasma membrane
| | Processus biologique | - negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- monocyte aggregation
- positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion
- hyaluronan catabolic process
- negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator
- interferon-gamma-mediated signaling pathway
- extracellular matrix disassembly
- extracellular matrix organization
- negative regulation of apoptotic process
- cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus
- positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
- cartilage development
- adhésion cellulaire
- negative regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
- cell-matrix adhesion
- positive regulation of monocyte aggregation
- leukocyte migration
- neutrophil degranulation
- wound healing, spreading of cells
- regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis
- cell-cell adhesion
- réponse inflammatoire
- migration cellulaire
- T cell activation
- positive regulation of kinase activity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000610
NM_001001389
NM_001001390
NM_001001391
NM_001001392
|
|---|
NM_001202555
NM_001202556
NM_001202557 |
| NM_001039150
NM_001039151
NM_001177785
NM_001177786
NM_001177787
|
|---|
NM_009851 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | NP_000601
NP_001001389
NP_001001390
NP_001001391
NP_001001392
|
|---|
NP_001189484
NP_001189485
NP_001189486 |
| NP_001034239
NP_001034240
NP_001171256
NP_001171257
NP_001171258
|
|---|
NP_033981 |
|
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 11: 35.14 – 35.23 Mb | Chr 2: 102.64 – 102.73 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|

 Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire 



















